300 novelties
to fully satisfy you
LEAN tools and approaches
SMED is a method of analyzing processes to provide a basis for optimization to save up to 80% of changeover time.

SMED is an acronym for Single, Minute, Exchange, and Die.

Single, Minute, Exchange, and Die can be understood as a metric of change per minute. More realistically speaking, we often hear the term “single digit”, which signals a single number format like 1, 4, 8, etc... Therefore, this is a tool to measure change in less than 10 units. This can be 9 seconds, 9 minutes, or 9 hours; dependent on the intensity of change which is implemented. In all cases, the goal is the same, it is to reduce the lead time it takes to change a tool, and the time it takes to move from point A to point B.
Lean methodologies can be schematically represented in the form of a house made up of several building blocks that harmonize with one another with a similar end goal, which is to better serve customers and meet their expectations more effectively.
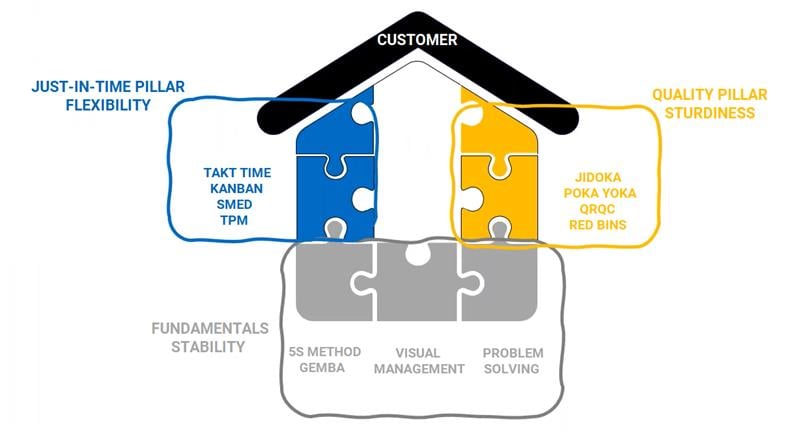
This house shaped representation of lean by popularized by the Toyota Motor Corporation, which is one of the reasons it is referred to as the “Toyota House”. The basic tools that ensure the stability of the house are found at the base of the structure, acting as a bedrock for the entire methodology.
When incepting Lean methods, these approaches must be put in place as a priority to ensure good stability for the rest of the given procedures. These fundamentals include:
Once the fundamentals are in place, building the quality pillar ensures the best possible production quality and makes all production processes more robust. This includes:
Once the fundamentals and quality pillars are in place, we can start constituting the “flexibility” pillar. This pillar makes it possible to better adapt to customer demand. This includes:
The SMED method is a methodology for alterations changing within production. Today, product manufacturing is generally very diversified and customizable, which makes it necessary to switch production from product A to that of product B.
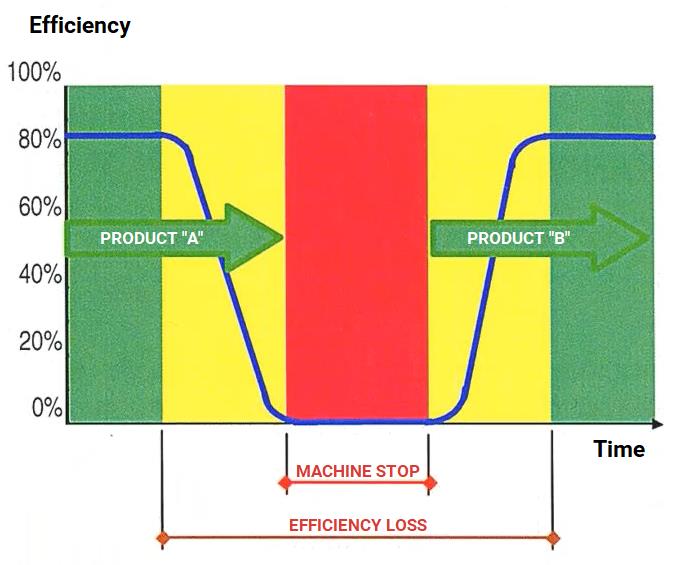
To achieve this, it is necessary to have some down time within the production/factory line. This generally leads to an idle time, which is a time in which the machine is not producing. This “idle time” is called Muda, a French word that translates to “waste”. To achieve excellence in production, Muda requires elimination or minimization. IN the traditional context, this idle/down time can be broken down into several stages:
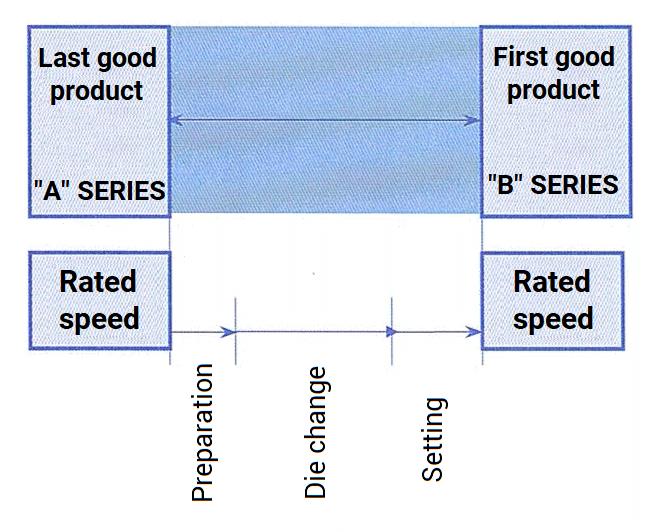
The SMED time is calculated between the production of the last acceptable A product and the first acceptable B product. This method analyzes this sequence of tasks and then identifies the sources of progress, allowing the reduction of these less productive times.
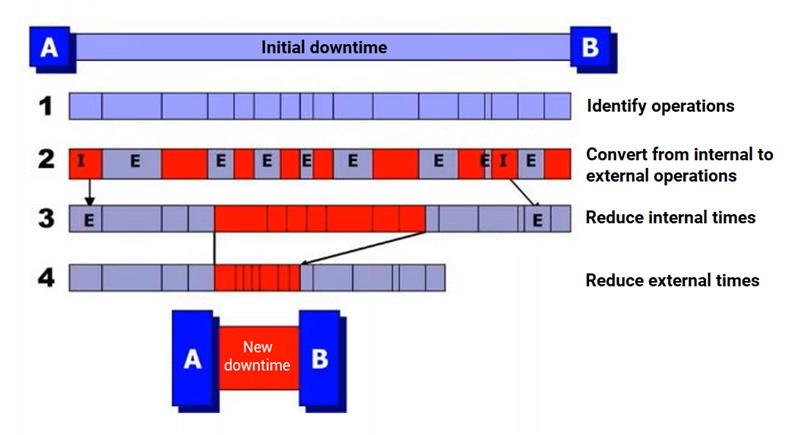
SMED tools are used within a team. All members must be involved and understand the process in order to make necessary suggestions. Stakeholder collaboration is necessary, and lone the team is typically trained in the SMED method.
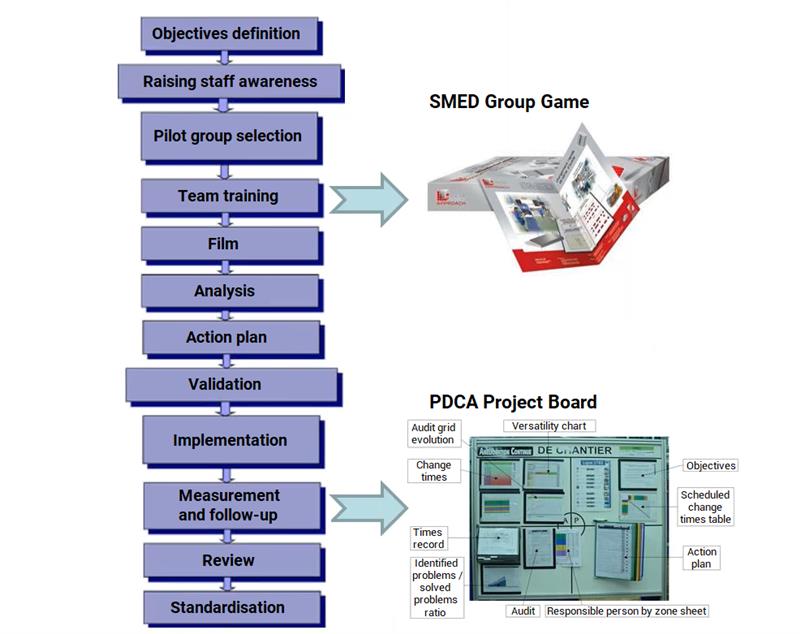
Throughout the training, usage of the SMED training game is ideal; it assists each member of the team to understand the process and take a proactive approach.
Once the team is trained, we can apply the 5 steps of the SMED method.
This application should be verified and monitored to ensure that it works properly. It is recommended that a PDCA worksite board is used, mainly for Visual Management.
The application of the SMED methodologies allows for the following benefits:
Indirect Benefits include:
The main risk of the SMED method is misunderstanding implementation. Indeed, the SMED method is poorly applied, stakeholders tend to implement to go very quickly. This can generate safety risks and stress for operators. This can also be counterproductive as safety at work is reduced and increased stress among operators can generate work slowdowns incompatible with overall well-being at the workplace. On the contrary, although the goal of the SMED method is to save time, this time should not be saved by working faster, rather by working more efficiently.

Duration: 2 hours to 2.5 hours
Participants discover and become aware of the possibilities for improvement and the virtues of an analysis of the organizational process.
Don’t wait any longer to train your employees in SMED through play.
The Starter Kit Worksite Case: Instant and simple creation of an SMED monitoring table as part of a pilot project following the game.
Results – a collective, shared, and effective success.

Discover all the concrete applications, tools to implement as well as our advice on our areas of expertise.
Do not hesitate to contact us if you would like more information or customized support.
Our experts are at your disposal.