300 novelties
to fully satisfy you
LEAN tools and approaches
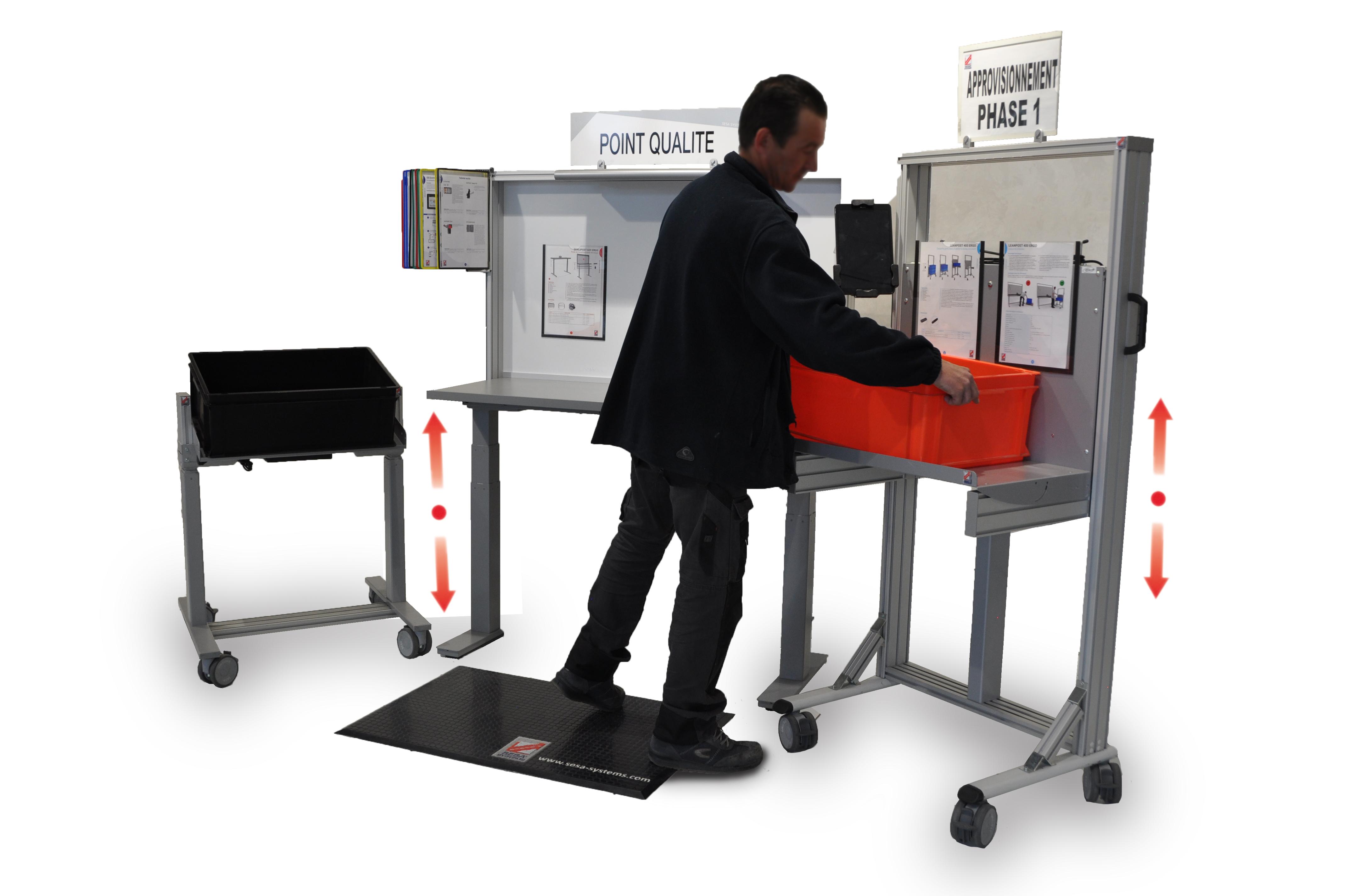

Quick Response Quality Control (or QRQC) is a method strongly inspired by Lean Management. Like many methods derived from Toyotism, the QRQC aims to treat defects as soon as they appear. In a way, this concept is very similar to that of Poka-Yoke. Popularized by Nissan in the 90s, the QRQC is a real revolution in the way it deals with logistics and production problems.

Unlike Lean methods inspired by Toyotism such as the 5S which aims at "zero defects", the primary goal of a QRQC approach is to resolve technical failures as quickly as possible as soon as they appear. For this, operators do not hesitate to solicit their hierarchy. This is what makes this Lean Management tool special: all the components of an organization are an integral part of the process. The greater the difficulties/defects encountered, the more the information will rise "high" in the hierarchy. Similarly, the higher the financial stakes, the higher the information will go up as well. "To the great evils the great remedies". In short, it is a very pragmatic approach to the field that goes so far as to permeate a managerial mode. An important aspect of the QRQC is the share of autonomy granted to employees. With the principle of QRQC, it is estimated, in fact, that the competence that makes it possible to solve a problem is as close as possible to the field. Thus, the QRQC simply corresponds to a treatment of defects as soon as they occur and at their place of occurrence. The operators/collaborators involved in the anomaly are also the ones who overcome it.
Like many principles of Lean Management, the QRQC comes in a few key ideas. We will divide them into 2 categories: those relating to "Quality Control" and the others dedicated to "Quick Response". The first step is to control the quality of the products and establish the real nature of their defects. This state of mind corresponds to the "San Gen Shugi": "real place, real room and real data".
To these preliminary steps is then added an action step: the "Quick Response". As its name suggests, it aims to respond as quickly as possible to the problem raised.
In the context of the QRQC, we place a lot of value on the feedback of information. If an operator fails to solve a problem within a given time (often 24 hours), then he goes back to the higher hierarchical level. The QRQC then subjects this new level to a time limit to deal with the problem. Once the difficulties have been overcome, the information goes back down in the opposite direction: from the management/managers to the operators. The purpose of this flow of information is: coaching and prevention. The goal is obviously not to repeat the same mistakes in the future.
Most often, companies favor 3 levels of information :
To be able to make a significant human and financial investment.. To be effective, the QRQC cannot be limited to a few teams. It must be applied throughout the company. This requires a significant investment to train all employees on this subject. The goal is to ensure that a large part of the industrial ecosystem of which we are part applies the QRQC method.
Valuing everyone's human and personal skills.Administrative burdens should be avoided at all costs and the pragmatism of employees is necessary.
Manage to maintain the improvements made and a "QRQC state of mind".The QRQC is a Lean Management tool that only reveals its full potential in the long term. The entire company must support the QRQC initiative for it to function properly.

Discover all the concrete applications, tools to implement as well as our advice on our areas of expertise.
Do not hesitate to contact us if you would like more information or customized support.
Our experts are at your disposal.