What is LEAN Logistics?
Lean Logistics is a supply chain and logistics operations management method aimed at maximizing efficiency by reducing waste. Inspired by the principles of Lean Management, initially developed in the manufacturing sector by Toyota, this approach focuses on continuous improvement and creating value for the customer while minimizing the resources used.
What are the Principles of Lean Logistics?
- Elimination of Waste: Lean logistics identifies and eliminates "mudas" (waste) in the logistics process. There are seven types of waste typically targeted: overproduction, waiting time, transport, unnecessary processes, excessive warehouse stock, unnecessary movements, and defects.
- Continuous Flow: Creating a continuous flow of materials and information is essential. This involves synchronizing processes so that materials move without interruption, thereby reducing delays and in-progress stock while increasing performance.
- Pull System: Instead of producing in large quantities to store, the "pull" system means producing and transporting goods in direct response to customer demand. This approach better meets actual needs and reduces unnecessary stock.
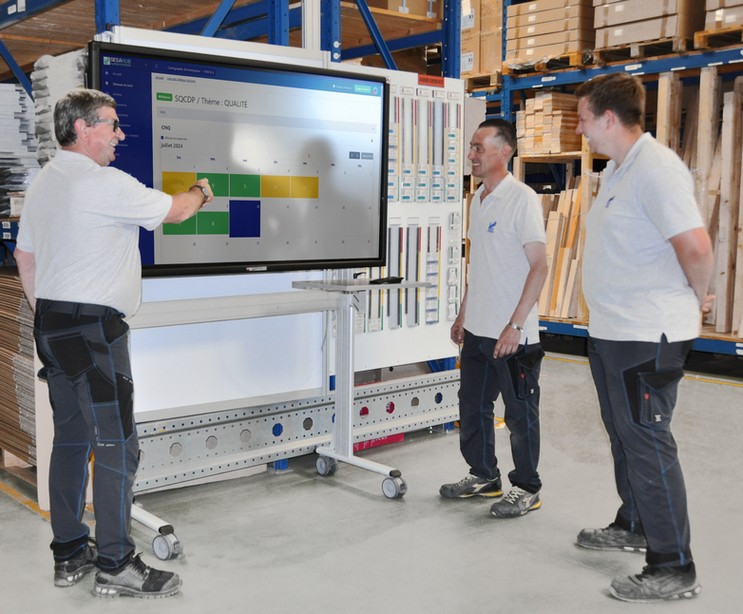
- Kaizen (Continuous Improvement): The Kaizen culture encourages all employees to continuously seek ways to improve logistics processes. This can involve small daily adjustments or larger initiatives.
- Respect for People: Lean logistics values the contributions of all employees. Teams are encouraged to collaborate, share ideas, and be autonomous in problem-solving.
How to Implement Lean Logistics?
To implement Lean logistics in a company, several steps and tools are necessary. This process can be broken down into multiple tasks:
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM): This technique involves visualizing the entire supply chain process to identify waste and improvement opportunities. VSM helps understand the flow of materials and information.
- 5S (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain): This method organizes the workplace to make it more efficient and safer. By applying the 5S, companies can reduce wasted time and improve productivity.
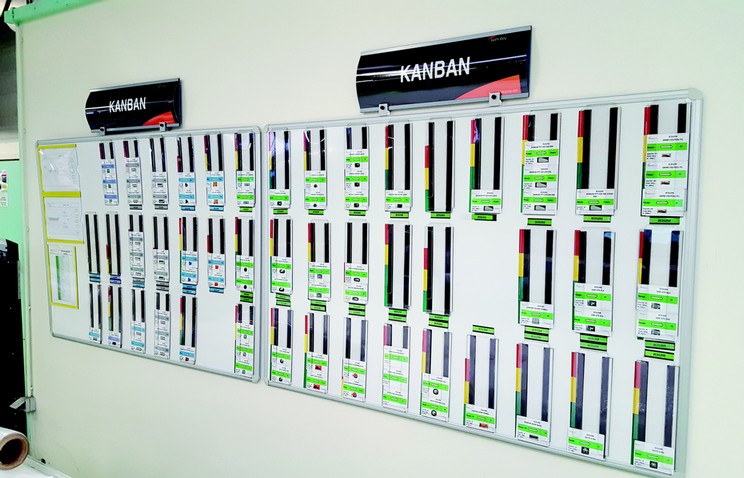
- Kanban: A visual system that controls production flow using cards or signals. Kanban helps manage stock levels and avoid overproduction.
- Just-in-Time (JIT): Produce only what is necessary, when it is necessary, and in the necessary quantities. JIT reduces storage costs and improves responsiveness to customer demands.
- Work Cells: Organizing teams and machines in a way that minimizes movement and waiting time. This enables a smoother and faster production flow.
What are the Benefits of Using Lean Logistics?
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating waste and optimizing processes, companies can reduce operational costs.
- Improved Quality: Focusing on continuous improvement and reducing defects leads to better quality products and services.
- Increased Responsiveness: A more agile logistics system allows better responses to demand fluctuations and customer requirements.
- Employee Satisfaction: Involving employees in process improvements fosters a more collaborative and motivating work environment.
- Customer Satisfaction: By offering better quality products and reducing delivery times, companies can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.

Key Takeaways…
Lean logistics provides a systematic approach to improving the efficiency and responsiveness of supply chains. By implementing Lean principles, companies can not only reduce costs and improve quality but also create a more engaging work environment for employees and offer a better customer experience. Adopting Lean logistics requires a commitment to continuous improvement and a company culture focused on collaboration and respect.